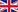
Recognize the Asian long-horned beetle and its symtoms
Is the Asian long-horned beetle (ALB) a dangerous pest?
The Asian long-horned beetle (Anoplophora glabripennis Motschulsky) is not harmful to human beings (it does not bit, it is neither irritating nor poisoning), but it can seriously damage trees. Indeed this beetle can kill an healthy tree in few years.
Is the occurrence of an ALB outbreak the Marche Region a real risk?
In August 2013 an outbreak of ALB, was found in the Marche Region in the province of Fermo. The infested trees and the close host plants have been cut and chipped and more plants will be processed in the same manner if infested by the pest. Further investigations are currently undertaken to accurately detect the occurrence of the pest. The general awarness about this problem allows to early detect new infestations and prevent the spread of this dangerous beetle.
How to detect the adult? How big is it?
ALB is a long horned beetle, adults belonging to the family of Cerambycidae or Coleoptera range from 25 and 35 mm in length, antennae excepted. It is shiny black with white or sometimes light beige spots on the elytra.
What are its characteristics?
Besides its size and color, typical features of this beetle are the very long antennae (at least as the body) that can reach 80 mm in length. They are divided into 11 elements, which are black with light rings (white to bluish grey).
Can it be confused with other insects?
Yes: with several large beetles , even if they are not threatening. In the Marche region, the Asian long-horned beetle is the only species with a body between 25 and 35 mm long, black with white spots on the elytra and antennas with white or bluish grey rings.
Are the larvae recognizable?
Females of the Alb lay eggs only in living wood. The larvae dig galleries into the wood (wood borers), are creamy white, without legs, with brown front chest, up to 5cm long when fully developped.
Larvae complete development has been recorded both on living and dead trees. The larvae are however hard to distinguish from those of other big size beetles. For example white larvae, that can be observed in the soil or in the wood dead since more than 2 years, are not larvae of ALB but probably of native non-harmful beetles.
Which trees are attacked?
As far as known, the Asian long-horned beetle attacks trees of any age, even perfectly healthy, with trunk and branches with a diameter larger than 1cm. The favoritepreferite host species are: maple, birch, horse chestnut, poplar, elm, willow but many other potentially many other broad-leaved species have been observed as not common susceptible plants in the world.
When can a tree be suspected as infested?
The symptoms are often visible at the height of the first branches. According to the current knowledge, the base of the trunk and branches with a diameter lower than 1 cm, are not attacked.
The symptoms are:
- circular holes (diameter 10 to 13 mm) ALB the exit holes of the adults (in our Region some native insects can produce exit holes in the wood, which are, however, of irregular shape and/or different size);
- multiple oviposition pits: are depressed funnel-shaped cavities (with serrated and ovoid edge and with a 10-15 mm diameter) excavated by the female by means of her mandibles. Then the female introducing the ovipositor into the pit, lays an egg under the bark;
- sap oozing from oviposition pits;
- sawdust more or less fine (depending on the age of the larvae producing it), piled up in the infested branch junctions or on the ground;
- adult feeding damages Adults of ALB feed themselves of twigs and leaf petioles evidently eroding the bark tissues.